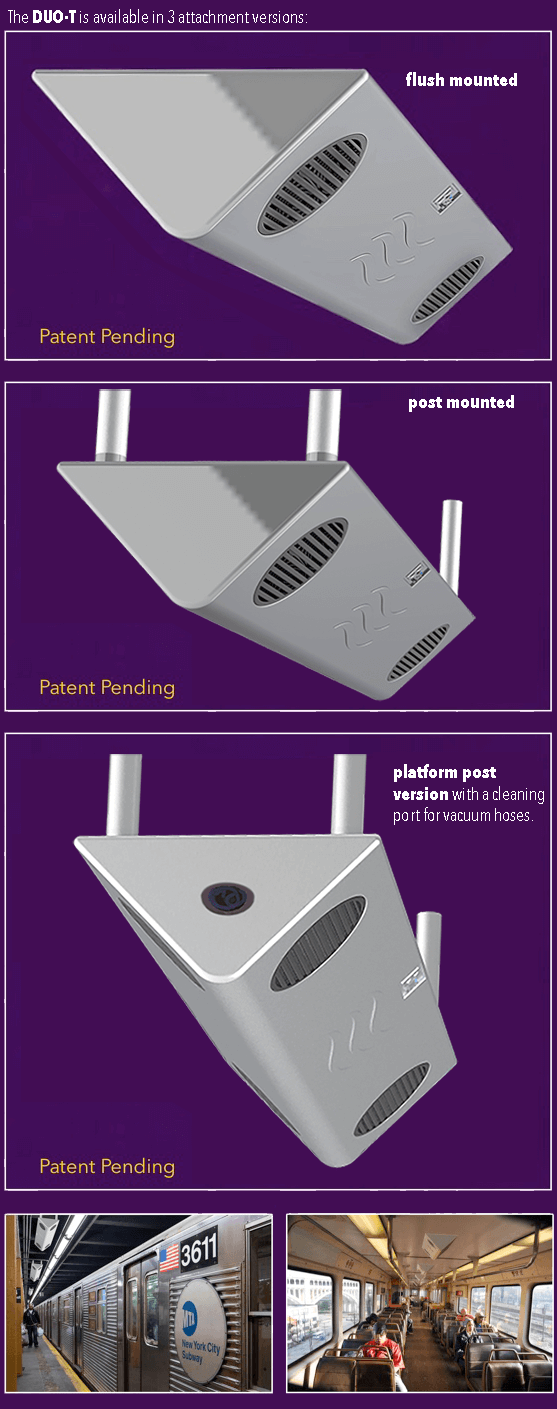
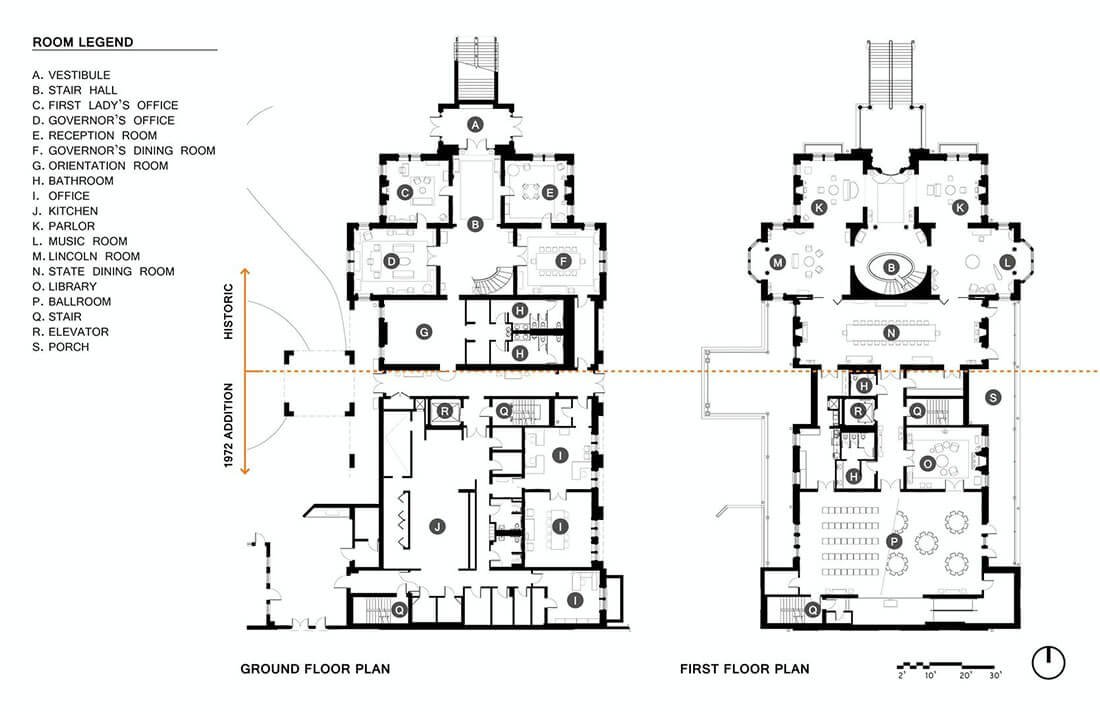
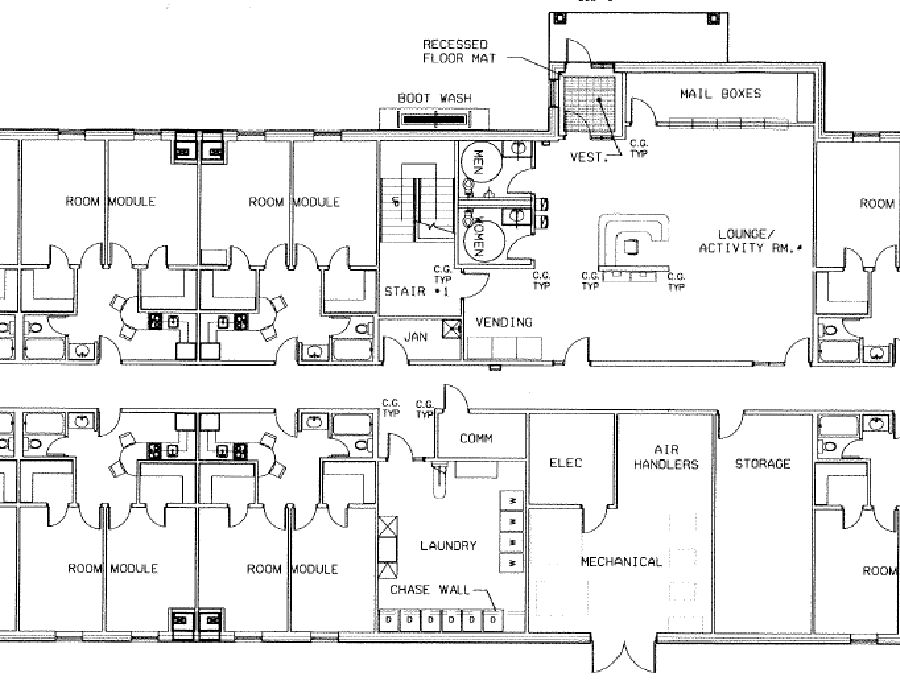
The Science
Making The Air Safe To Share™
All pathogens have one thing in common: they all have a DNA system.
UVC is quite deadly to the tiny pathogens.
Scientis have known for some time now that the bonding process between the Amino acids and proteins can not be sustained while the DNA is being bombarded by the tiny but extremely powerful UVC photons.
The wavelenghts that have the greatest deadly affect on the DNA are between 200nm and 283nm.
There are several other contributing factors to making the process complete: distance of the light and its intensity as well as length of time. All those factors are called the FLUENCE.
Why UVC?
UVC has been proven to be the most effective pathogen sterilization method.
But it’s also been shown to be harmful to people who are in a room treated
with UVC rays.
So…
Blisk® conceived and developed a series of products that utilize UVC, but were made as enclosures in which we sterilize the pathogens by guiding the air we share and masking it safe.
We ‘lock’ the harmful light inside our enclosures with a patented light breaking vent, we call the LB Vent, then we bombard the inside space with mega doses of UVC rays that inactivate even the most resistant pathogens by controlling the length of time the air is “under the gun.”
To the pathogens it’s as if a series of huge nuclear explosions enveloped them. There’s no way out for the pathogens except get inactivated.
Why is UVC so effective?
UVC targets the DNA of the pathogens. They all have that in common. Some require a longer dose, while others like COVID 19 the shortest!
“Light is a more powerful Pathogen Killer than chemicals”
David J. Brenner, Ph.D.
Columbia University Institute of Radiology,
Irwin School of Medicine, New York, NY
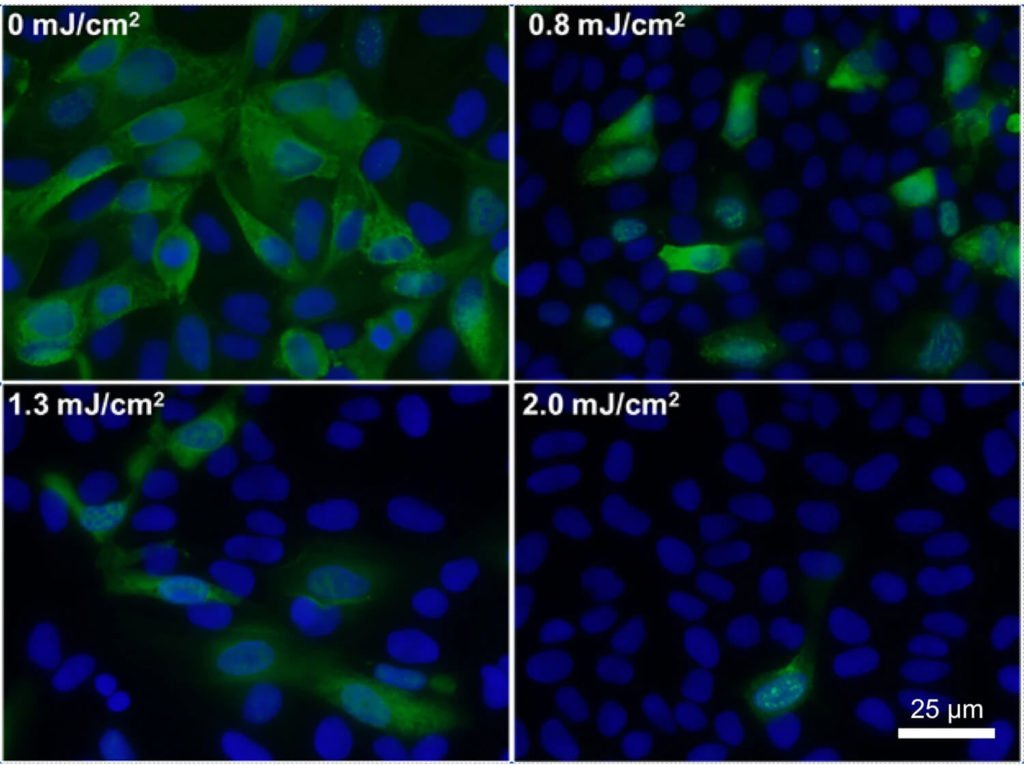
Manuela Buonanno, David Welch, Igor Shuryak, David J. Brenner all of the Center for Radiological Research, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, New York 10032, USA
The 4 images above define visually the passage of time from zero to 2.0 seconds using the same pathogens and the result from under a 40X microscope after the pathogens were exposed to the same amount of light from the same distance.
Image 1 equals 0 time elapassed
Image 2 equals .8 seconds elapsed
Image 3 equals 1.3 seconds elapsed
Image 4 equals 2.0 seconds elapsed
The amount, or strength of UVC light was equal to 2/1000 of Joule (a unit of light in the sub watt p/sec. amt.)
The total area shows various pathogens in green, and no pathogens in blue. Gradually, as the exposure was increased a greater part of the area was changed to blue, or dead pathogens… plainly, inactivated.
Airborne-mediated microbial diseases such as influenza and tuberculosis represent major public health challenges. A direct approach to prevent airborne transmission is inactivation of airborne pathogens, and the airborne antimicrobial potential of UVC ultraviolet light has long been established; however, its widespread use in public settings is limited because conventional UVC light sources are both carcinogenic and cataractogenic.
The Blisk® X Series
Our X-Series Air Sterilizers will deliver the same deadly blow to the pathogens regardless of their resistanceto lower doses. Blisk® offers plug and play systems that are equipped with computerized controls to accomplish this 24/7 regardless of the pathogen, even as common as the annual flu.
BuildYourSystem
Air Sterilization andVentilation With UVC

Property Type
Will this SYSTEM BUILD be for a
GOVERNMENT ENTITY, or a
PRIVATE ENTERPRISE?